← Blog
/
Data annotation tools as the foundation of reliable AI models
Hybrid data generation blends scale and quality for better training
The AI field is growing rapidly, with more sophisticated models being rolled out almost daily. In the midst of all this, the powerful algorithms that fuel these models steal the show, and people tend to forget the data side of things. In practice, AI systems are advanced right at the pipeline phase, where raw data from which they learn is interpreted and annotated.
Data annotation tools play quite a big role in transforming unstructured raw data like text, images, audio, and video into machine-readable signals that models can meaningfully learn from. Data preparation is one of the most essential steps in AI model training, and here’s where the need for rigorous annotation manifests. Machine learning models rely heavily on high-quality annotated data to learn patterns, make accurate predictions, and perform effectively in real-world applications. This begs for top-of-the-game data annotation tools.
The best data annotation practices and tools support a wide range of annotation tasks and, at times, offer advanced features like auto-annotation and AI assistance. Apart from these performance features, such tools should be easy to use because annotation is done even by non-technical individuals. So, data annotation tools should at least provide a user-friendly interface that streamlines the labeling process for users of all expertise levels.
Owing to the growing interest in data annotation in advancing the field of AI, we could take a moment to dive deep into the critical functions of data annotation tools and their key characteristics. In so doing, we will learn why platforms like Toloka represent a modern, scalable solution for today’s challenges in machine learning and computer vision.
Why Data Annotation Is the Backbone of AI
We have already highlighted that data annotation is essential because it helps AI understand and process raw data. Data annotation is essential because it helps machine learning models process raw data.
High-quality training data determines model performance, and inaccuracies in the annotation process lead to misinterpretations, reducing reliability. For these reasons, data annotation has become more critical as systems require larger volumes of annotated data.
The reliability of computer vision models is directly tied to the quality of the data they are trained on. Accurate data annotation enables the development of capable models and fosters advancements in AI and machine learning. Data scientists often oversee this process, selecting the right data annotation tool to ensure high-quality datasets. However, choosing the right data annotation tool can be difficult given the many options available.
Data annotation supports the foundations of AI, including natural language processing and computer vision. When choosing annotation tools, it is imperative to consider the model type.
For language models, a text annotation tool suffices, while vision models require tools that support the annotation of image and video data. Platforms like Toloka handle both with sophistication and quality.
Why Data Annotation and Labeling Tools Matter
Preparing data for AI training requires a labeling tool that ensures quality and gets the work done. Data annotation, also called data labeling, involves adding metadata and tags to raw data to provide context for algorithms. Effective data annotation tools are categorized by project needs, guaranteeing data quality control and efficient data management.
Quality control is essential for accuracy, while the choice of data format is critical for compatibility with various frameworks. Thus, data annotation and labeling tools make it easier for machine learning algorithms to understand the data. In supervised learning, a labeling platform that manages diverse data types is a data scientist's best friend.
Efficiency is a key criterion. Because manual annotation can consume significant resources, teams need high-performing tools. The right data annotation tool must balance functionality with the need to label data quickly and accurately.
How Data Labeling and Model Training Connect
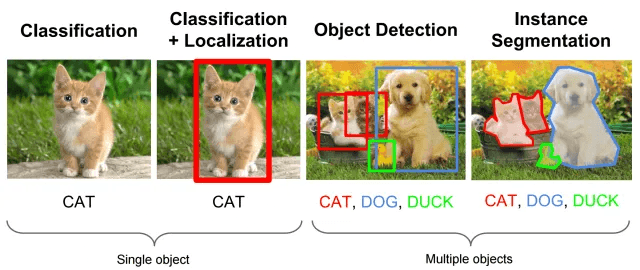
It is now clear that AI performance is proportional to the rigor of the training data annotation, notwithstanding the algorithm used. At the heart of this connection lies data labeling. This can include image annotation for computer vision, video annotation for object tracking, or text annotation for natural language processing.
Accurate data labeling ensures that AI models learn patterns and generalize to new data. In image annotation, drawing bounding boxes or performing image segmentation enables models to excel at object detection and image classification. Similarly, detailed video annotation allows for robust object tracking, while high-quality text annotation is essential for sentiment analysis.
Effective annotation makes it easier for the algorithm during model training. The better the annotated data, the more reliable the resulting machine learning models. Poorly labeled data introduces bias and reduces accuracy.
Therefore, the best data annotation tools must streamline the labeling process, support various annotation tasks, and ensure consistency at scale. By meeting these needs, the model training process is accelerated, resulting in trustworthy AI models.
Core Functions of a Data Annotation Platform
Aside from the general functionality of adding structure to the training data, it is important to go deeper and understand the core of data annotation tools in terms of their workflows and input and output layers.
In terms of their input data types, most annotation platforms accept text, image, video, and sensor data. They organize the data, depending on the type, and output training-ready datasets.
Functionally, many modern platforms for annotation offer online annotation tool features and web app interfaces. This makes them accessible from any browser and facilitates collaboration.
A platform that offers collaboration and accepts diverse data types is, therefore, already top of the list for a data scientist looking to make the right choice.
Multimodal Support and Industry Applications
Beyond workflow architecture and interface design, multimodal support and applicability across diverse use cases are key features to look for in any platform for annotation. Given the shift to multimodal AI, most annotation tools support multimodal data types, which allows teams to manage diverse projects on a single platform. For this reason, most data annotation tools have since allowed the integration of the various data types, including image, video, audio, text, and even LiDAR for point cloud data in a single AI training workflow.
These functionalities appeal to the various fields of AI development differently. For example, image annotation tools and video annotation tool options are widely used for computer vision tasks. Models that require image classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation used across industries like autonomous driving, healthcare, and agriculture will require tools that annotate images and videos with higher precision.
So, the core role of data annotation platforms is supporting the annotation process from raw data to usable datasets in a way that balances manual annotation with automation.
Common Data Types in Annotation Projects
While data annotation tools accept multimodal data for labeling, it is still important to look into the individual data types that most platforms work with.
Image and video annotation remain widely used in computer vision. Annotating video adds a temporal dimension, requiring frame-by-frame labeling jobs and tracking across video frames. Consequently, video data requires specialized annotation for object detection and event classification. Because videos consist of an entire image sequence, these tasks are similar to image labeling.
Text annotation is another pillar, supporting natural language processing tasks like sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, and text classification. A text annotation tool is frequently used to prepare data for chatbots and large datasets used in LLMs.
Audio transcription and annotation are essential for speech-based systems, including speaker identification and emotion detection. These are widely used in voice assistants and call-center analytics.
Sensor data, including LiDAR data, is increasingly important in robotics. LiDAR data supports 3D object detection and spatial mapping, enabling machines to understand depth.
All these data types form the foundation of most modern annotation projects. This is because many real-world systems rely on a combination of image, text, audio, video, and sensor data to train robust AI models.
Common Annotation Techniques: From Bounding Boxes to Segmentation
Different machine learning tasks require different annotation methods. These annotation techniques depend on two things: the task at hand and the data type in the workflow. Most of these techniques offer key points for human pose estimation and ease the overall data labeling workflow. Some of the widely used data annotation techniques supported by various annotation platforms are:
Bounding Boxes for Object Detection
One of the most common data annotation techniques is bounding boxes, which are fundamental for identifying object locations within images or video frames. They are widely used in applications such as autonomous driving, surveillance, and retail analytics. The image below shows bounding boxes in action.
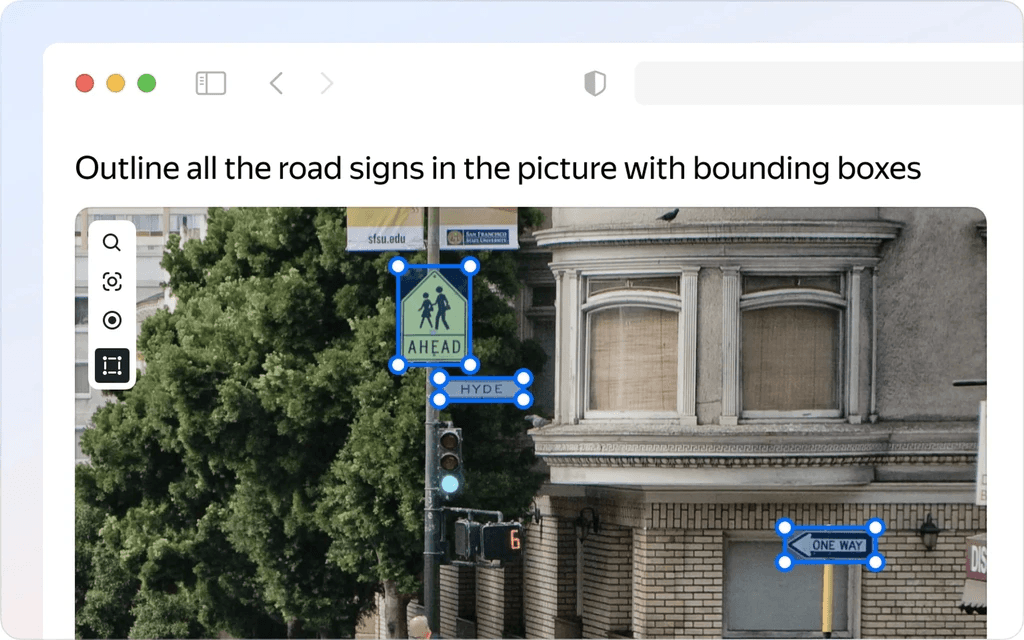
Bounding boxes for defining object boundaries are an image data annotation technique. (Source: Toloka.ai)
Image Classification and Object Tracking
Image classification is another data annotation technique that involves assigning a single label to an entire image. For example, identifying the pair of shoes below as boots and labelling it as such is image classification at play. Also tagging the images as relevant or not, depending on the search relevance, is an example of image tracking.

Image labeling in action. (Source: Toloka.ai).
On the other hand, object tracking as an annotation technique involves following the identified objects across video frames. These techniques are critical for activity recognition and motion analysis. For instance, identifying and classifying the cat as seen in this workflow and being able to follow it and identify it as such across various frames better explains object tracking.
Object tracking in action (Source: Medium)
Video Annotation Tool Workflows
A video annotation tool supports frame-by-frame labeling, temporal tracking, and event classification. These features enable models to understand dynamic scenes presented in typical video data.
Point Cloud Data and 3D Annotation
Point cloud data, often generated by LiDAR sensors, is also annotated differently. This data type is quite essential for robotics and autonomous systems. Accurate 3D annotation enables spatial reasoning and sensor fusion in complex environments, and involves proper and accurate mapping of data points, dimensions, and tagging.
The Annotation Process From Raw to Annotated Data
A typical labeling process starts with data ingestion, followed by task assignment and annotation. At the very top of this process is manual annotation, which ensures nuance. Human annotators set the wheel in motion by setting the parameters and pointing the workflow to the right edge cases. After this, automated annotation could be used to speed up initial labeling.
Some platforms offer auto-annotation features powered by AI, which can automate routine labeling tasks and improve efficiency. AI-assisted labeling is a major feature in modern tools, which involves utilizing pre-trained models and active learning to expedite the process and enhance consistency.
Automation features in data annotation tools can significantly reduce manual workload by using AI for tasks like auto-labeling and segmentation. The tool’s ability to accurately label data is essential for preparing high-quality datasets for supervised machine learning.
When dealing with large datasets, the annotation process must also integrate features for efficient data management. So, the annotation tool should also allow for importing, searching, and sorting. Such tools with cloud storage integration are the icing on the cake, as they help manage annotated data seamlessly.
Text Annotation Tool Use Cases in Machine Learning
To put the annotation process flow into perspective, we would take the example of text annotation for an NLP task. A text annotation tool supports natural language processing tasks such as text classification, sentiment analysis, and named entity recognition. It involves importing the data, classifying it, and annotating it to help models understand language structure, meaning, and intent.
High-quality text annotation is particularly important for:
Large language models
Generative AI systems
Multilingual and domain-specific applications
It is clear that as language models scale, consistent annotation guidelines and quality control become increasingly important.
Key Characteristics of High-Performing Data Annotation Platforms
When deciding on the data annotation tools to use on your project, some features stand out and take priority. Some of the features data science teams should consider are scalability, automation, support for multiple data types, quality control, user friendliness, transparency, fairness, and project management features.
Scalability
Owing to the increasingly growing data volumes and expanding project needs, teams need data annotation tools that are scalable. Teams should choose high-performing platforms that can grow with the project and also provide access to a diverse contributor base, since annotation comes along with the challenge of a global workforce.
Automation
The whole concept of data annotation tools was to cut down on the resource-intensive and time-consuming manual annotation. Therefore, within their workflows, these tools must support automation. In this case, Automated annotation and AI-assisted features reduce manual effort while maintaining precision. Annotation platforms must support rapid scaling, custom task design, and workflow automation.
Quality Control
Quality control mechanisms in data annotation tools include review workflows and consensus scoring to ensure data accuracy. Many platforms offer multiple QC methods, real-time monitoring, and analytics. Data quality control is essential to ensure the accuracy and reliability of annotations.
Support Multiple Data Types
As we have stressed over and over throughout this article, data annotation tools must be able to accept as input multimodal data. Since various teams work with different data on multiple projects, these platforms must be able to annotate all the possible types of unstructured data, like text, video, images, audio, and sensor data.
Transparency, Fairness, and Project Management
Leading platforms emphasize fairness and transparency for contributors, alongside robust project management features for requesters. Data annotation tools often provide project management features to facilitate team collaboration and task assignment. Most support cloud storage integration for managing annotated data efficiently.
User Experience and Interface Considerations
For these annotation tools, an intuitive user interface and customizable workflows enhance usability. User-friendly interfaces and customizable workflows are common features that improve efficiency for data annotators and teams.
User experience and interface design are critical for the efficiency of data annotation tools, impacting how easily users can perform annotations.
Challenges in Choosing Data Annotation Tools
Teams have to go through the hassle of balancing cost, functionality, and integration to finally end up with the right data annotation tool that suits their needs.
Individuals working on small pilot projects will require something not so pricey, while enterprises will focus more on platforms with integration capabilities with their existing machine learning pipelines and project workflows. The dilemma is quite a challenge, which brings forth the need for a data annotation tool that caters to all project sizes and needs.
Common Features Across Leading Platforms
Most platforms support basic techniques and data annotation needs, such as multiple data types and accelerated automation. Features like bounding boxes, polygons, and semantic segmentation are now integrated in most data annotation tools, with differences in advanced capabilities.
Also, most data annotation tools typically include features for dataset management, such as importing and cloud storage integration.
The Role of Automation in Overcoming Challenges
Since annotation tools cannot operate in isolation, introducing humans in the loop helps a great deal in streamlining the annotation workflows. Hybrid human + AI workflows address scaling issues and guarantee accuracy because of the combined supervision and speed.
Automation features, such as AI-assisted labeling, enhance efficiency, while quality control mechanisms are essential to ensure annotation reliability.
Toloka as Your Go-to A Scalable Data Annotation Platform
Toloka stands out as a modern data annotation platform that combines a large global crowd, advanced automation tools, and scalable pipelines to support projects of any size. This cutting-edge platform focuses on high-quality human expert data for generative AI, LLMs, RLHF, instruction tuning, and computer vision. The most outstanding features of Toloka are its AI-guided setup and always-on LLM-based quality assurance.
Toloka offers flexible annotation for text, images, video, audio, and more, which aligns perfectly with industry needs in machine learning and computer vision applications.
Toloka's Support for Diverse Training Data Types
Toloka handles complex annotation tasks for text, including NLP tasks such as entity recognition and sentiment analysis. It also supports audio, images for image annotation and image classification, as well as annotating video for object tracking.
It supports multimodal projects and point cloud data in certain configurations, which makes it suitable for diverse data types in machine learning models.
Built-In Quality Control in Toloka
As a plus, Toloka features built-in quality control like automated validation via tuned LLMs, multi-step reviews, and real-time quality monitoring.
The platform’s LLM QA continuously validates outputs, iterates on feedback, and ensures consistent and accurate annotations.
Customizable Workflows and Task Design
Toloka provides rich templates for annotation tasks, customizable task interfaces, and AI-assisted project setup. Users describe tasks in natural language, and the AI agent builds full projects, including guidelines and UI. Its pilot tasks feature allows evaluation of instructions before full launch.
Integrations and Pipeline Support
Toloka’s API-driven pipelines enable seamless integrations with ML tools. It also provides real-time analytics and monitoring, which support efficient model training.
Benefits for Machine Learning Teams Using Toloka
As a platform, Toloka enables faster dataset production through hybrid human-AI workflows. Higher label quality comes from expert tiers and structured QC.
It gives access to global expertise and supports multilingual and domain-specific data, ideal for natural language processing and specialized computer vision tasks.
On top of all these, Toloka has predictable costs, with no minimums or contracts, which make it accessible compared to traditional vendors.
Why Toloka is the Best Data Annotation Tool to Ensure Transparency and Fairness
Toloka prioritizes transparency for requesters with clear pricing and compliance as per SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, and ISO 27001 guidelines. Fairness for contributors includes ethical practices and opportunities worldwide. This makes Toloka the ideal tool for all your annotation needs.
Final Word on Data Annotation Tools
Data annotation tools are no doubt indispensable for building reliable AI models. As demands grow for high-quality training data in machine learning and computer vision, platforms like Toloka provide the scalability, quality, and flexibility needed to get the work done.
Combining expert human input with advanced automation, Toloka helps machine learning teams produce better datasets faster. This drives innovation in computer vision applications and beyond.
When all is said and done, investing in a robust data annotation platform ensures long-term success in an AI-driven world, especially with ongoing trends toward hybrid workflows and ethical data practices.
Quality data isn't optional — it's the foundation. Toloka Platform combines human expertise across 90+ fields with AI-powered quality assurance, delivering clean, validated annotations for your most demanding AI projects. Our AI Assistant helps you define precise requirements, and the Toloka Quality Loop guarantees production-grade results. Start building with data you can trust.
Subscribe to Toloka news
Case studies, product news, and other articles straight to your inbox.
